MikroElektronika
IrDA2 click
IrDA2 click
SKU:MIKROE-1195
Couldn't load pickup availability
Share
IrDA2 click is a compact and easy solution for adding infrared communication to your device. It features TFDU4101 infrared transceiver module as well as MCP2120 infrared encoder/decoder from Microchip connected with the 7.3728 MHz external crystal. The click is designed to run on either 3.3V or 5V power supply. It communicates with the target board via UART interface and the following mikroBUS™ pins: AN, RST, CS.
Essential features
The combination of the TFDU4101 and MCP2120 results in support for fast and stable infrared data communication. The TFDU4101 infrared transceiver module covers the full IrDA range of more than 1m and speed up to 115.2 kbit/s.
Application
With low power consumption, all these features make IrDA2 click ideal for TV and video systems, printers, fax machines, copiers, external infrared adapters, diagnostic systems and other industrial applications.
Key features
-
MCP2120 infrared encoder/decoder
- Up to IrDA standard 115.2 kbaud operation
- TFDU4101 infrared transceiver
- UART interface
- 3.3V or 5V power supply
Specification
| Type | Optical |
| Applications | IrDA2 board is ideal for wireless infra red data communication with PC remote controllers for home applicances and other devices. |
| On-board modules | MCP2120 infrared encoder/decoder, TFDU4101 infrared transceiver |
| Key Features | Data Communication rates up to 115.2kbaud. Interfaces with IrDA compliant transcievers with 1.63us Transmit/Receive format |
| Key Benefits | Low power consumption. Includes UART to IrDA standard bit encoder/decoder functionality |
| Interface | GPIO,UART |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | S (28.6 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on IrDA2 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
SMD jumpers
Jumpers J0, J1 and J2 connect MCP2120 controller BAUD0, BAUD1 and BAUD2 pins to VCC or GND. You can change baud rate settings by soldering J0, J1 and J2 in the appropriate position (Table 1). These jumpers are soldered in logic 1 position by default (9600 bps, software selection enabled). SMD jumper J3 is used to select 5V or 3.3V power supply (default position is 3.3V).
Table 1: Baud Rate selection
| B2 | B1 | B0 | Software selection | Hardware selection | Baud Rate (bps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | • | 9600 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | • | 19200 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | • | 38400 | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | • | 57600 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | • | 115200 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | • | 9600 |
Programming
Code examples for IrDA2 click, written for MikroElektronika hardware and compilers are available on Libstock.
Code snippet 1 - MASTER
This example demonstrates the functionality of the IrDA2 Click board.
The master initiates communication with the slave by sending 1 byte of data to the slave.
01 void main() {
02 ANSELC = 0; // Configure ports as digital I/O
03 ANSELD = 0;
04 TRISD = 0; // Set PORTD as output
05
06 i = 0; // Initialize global variables
07 received = 0;
08
09 UART1_Init(9600); // Initialize UART module at 9600 baud rate
10 delay_ms(200);
11
12 RC1IE_bit = 1; // Enable USART Receiver interrupt
13 GIE_bit = 1; // Enable Global interrupt
14 PEIE_bit = 1; // Enable Peripheral interrupt
15
16 UART1_Write(1); // Master initiates communication
17
18 while(1) {
19 if (received) { // If data received by Slave
20 LATD = i; // display it on the PORTD
21 i++; // Increment counter
22 received = 0; // Clear received flag
23 }
24 UART1_Write(i); // Send counter value to Slave via UART1
25 delay_ms(200);
26 }
27 }
Code snippet 2 - SLAVE
The slave accepts data, increments it and sends it back to the master.
The data received is shown on PORTD.
01 void main() {
02 ANSELC = 0; // Configure ports as digital I/O
03 ANSELD = 0;
04 TRISD = 0; // Set PORTD as output
05
06 i = 0; // Initialize global variables
07 received = 0;
08
09 UART1_Init(9600); // Initialize UART module at 9600 baud rate
10 Delay_ms(200);
11
12 RC1IE_bit = 1; // Enable USART Receiver interrupt
13 GIE_bit = 1; // Enable Global interrupt
14 PEIE_bit = 1; // Enable Peripheral interrupt
15
16 while(1) {
17 if (received) { // If data received,
18 LATD = i; // display it on the PORTD
19 i++; // Increment counter
20 received = 0; // Clear received flag
21 UART1_Write(i); // Send counter value to Master via UART1
22 }
23 }
24 }




New Products
-

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Pro Wide
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 117,969.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Pro Fixed Focus
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 106,719.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Pro Auto Focus
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 106,719.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Auto Focus
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 95,479.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Fixed Focus
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 95,479.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK 4 D Wide
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 106,719.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold outOAK-FFC IMX577 M12
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 8,499.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Pololu Ideal Diode Reverse Voltage Protector, 4-60V, 20A
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 329.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Pololu Ideal Diode Reverse Voltage Protector, 4-60V, 25A
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 439.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Pololu I²C Isolator, ISO1640
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 449.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
3pi+ 32U4 OLED Robot Kit with 30:1 MP Motors (Standard Edition Kit)
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 15,549.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Conductivity Calibration K 1.0 Set (4 pouches)
Vendor:Atlas ScientificRegular price Rs. 1,599.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Analog Discovery 3 Pro Bundle
Vendor:DigilentRegular price Rs. 42,569.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Lighthouse swarm bundle - Crazyflie 2.1+ (250mAh batteries)
Vendor:BitcrazeRegular price Rs. 474,999.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Loco Swarm bundle - Crazyflie 2.1+ (250mAh batteries)
Vendor:BitcrazeRegular price Rs. 544,999.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Kopis X8 Cinelifter 5" Kit - Caged (Frame Kit)
Vendor:HolybroRegular price Rs. 28,199.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Atlas Scientific i3 InterLink
Vendor:Atlas ScientificRegular price Rs. 6,349.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
PoE Injector
Vendor:LuxonisRegular price Rs. 2,099.00Regular priceUnit price / per -

 Sold out
Sold out1-Port VINT Hub Phidget
Vendor:PhidgetsRegular price Rs. 2,699.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Power Distribution Board (PDB) Board (With XT30 Pre-soldered)
Vendor:HolybroRegular price Rs. 1,099.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Holybro 1045 Propeller 2 Pair CW+CCW-Black
Vendor:HolybroRegular price Rs. 1,549.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
ACS37220LEZATR-100B3 Current Sensor Large Carrier -100A to +100A, 3.3V
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 829.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
CT433-HSWF50MR TMR Current Sensor Compact Carrier -50A to +50A, 3.3V
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 1,039.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
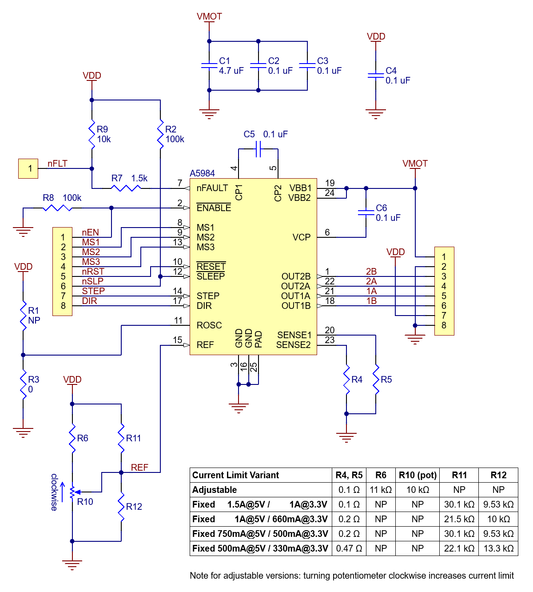
A5984 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier, Adjustable Current, Blue Edition
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 409.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
A5984 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier, Fixed 1A@5V / 660mA@3.3V, Blue Edition (Soldered Header Pins)
Vendor:POLOLURegular price Rs. 489.00Regular priceUnit price / per