Join the club
Get exclusive deals and early access to new products.

POLOLU
This USB-to-serial adapter lets you easily connect a TTL serial device to a PC by acting as a virtual serial port. The board is a Micro-USB carrier for the Silicon Labs CP2104 USB-to-UART bridge that provides access to all of its control signal pins and GPIO pins.
This USB-to-serial adapter is a breakout board for the Silicon Labs CP2104 USB-to-UART bridge, and it is a great solution for connecting microcontroller projects and other logic-level serial devices to a personal computer. The tiny unit measures only 0.6″ × 0.95″ including its Micro-USB connector. It offers several options for accessing the data, control, and GPIO pins on the CP2104, all of which are made available on a 0.1″ spacing.
This board uses 3.45 V signal levels by default, but the signal pins can tolerate higher voltages, allowing the adapter to be used with 5 V systems that see 3.45 V as a logic high. The green LED on the SUSPEND line indicates an active USB connection when lit.
The adapter looks like a standard virtual serial port (COM port) to the computer’s operating system, which means it can be used with any software designed to work with a serial port (even a legacy RS-232 port). The CP2104 is a full-speed USB 2.0 device and allows baud rates of up to 2 Mbps. Drivers are available from Silicon Labs for Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Linux, and Mac OS X.
This product requires a USB A to Micro-B cable (not included) to connect to a computer.
For a similar adapter with a USB Mini-B connector, please see the Pololu USB-to-Serial Adapter.
Specifications
Using the adapter
Pinout
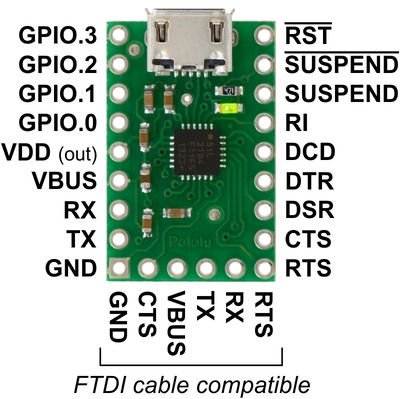 |
| Pin | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| VDD | Power | 3.45 V voltage regulator output |
| VBUS | Power | USB bus voltage (5 V) |
| GND | Power | Ground |
| RST | In | Device reset |
| TX | Out | Asynchronous serial data transmit (idle high) |
| RX | In | Asynchronous serial data receive |
| CTS | In | “Clear to send” control input (often used with RTS) |
| RTS | Out | “Ready to send” control output (often used with CTS) |
| DSR | In | "Data set ready" control input (active low) (often used with DTR) |
| DTR | Out | "Data terminal ready" control output (active low) (often used with DSR) |
| DCD | In | "Data carrier detect" control input (active low) |
| RI | In | "Ring indicator" control input (active low) |
| SUSPEND | Out | Driven high when in USB suspend state |
| SUSPEND | Out | Driven low when in USB suspend state (connected to green LED) |
| GPIO.0 | I/O | User-configurable inputs or outputs (one-time programmable) |
| GPIO.1 | ||
| GPIO.2 | ||
| GPIO.3 |
Connections
All of the adapter’s pins are available in two rows spaced 0.5″ apart along the sides of the board. This allows any pin to be accessed easily while the adapter is plugged into a solderless breadboard, as shown in the left picture below.
Alternatively, a 1×6 header can be soldered to the end of the board, as shown in the right picture below. This gives access to six signals (RTS, RX, TX, VBUS, CTS, and GND) that are commonly found on FTDI cables and other similar USB-to-serial adapters. As a result, this CP2104 adapter board can be used as a drop-in replacement for an FTDI cable in many applications, such as programming Arduino-compatible boards.
|
|
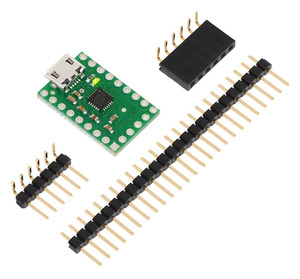
The carrier board ships with a 1×25 straight male header strip, a 1×6 right-angle male header strip, and a 1×6 right-angle female header as shown below. You can also solder wires directly to the pads for the smallest installation.
 |
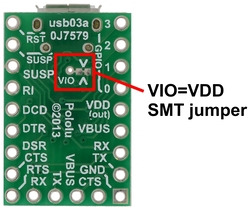 |
This carrier board connects the VIO pin of the CP2104 to VDD by default, setting its logic voltage level to the 3.45 V provided by the IC’s built-in voltage regulator. If you want to use a lower logic voltage, you can disconnect VIO from VDD by cutting the thin trace between the two pads of the surface-mount jumper shown to the right. You can then solder a thin wire to the exposed via labeled “VIO” and connect it to a separate voltage supply (as low as 1.8 V).
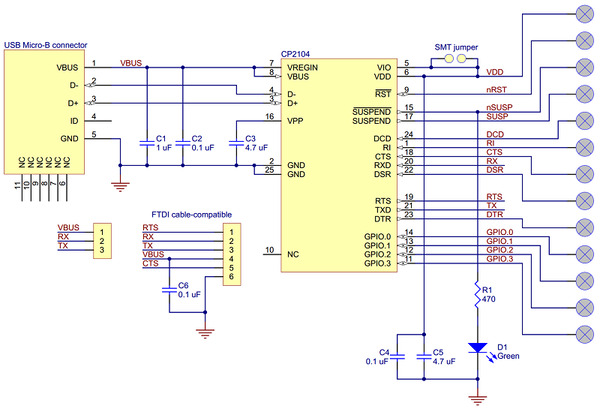
Schematic diagram
 |
Dimensions
| Size: | 0.6″ × 0.95″ × 0.17″1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 1.4 g2 |
General specifications
| Baud: | 300 bps–2 Mbps |
|---|
Notes:
1. Without included optional headers. This measurement includes the USB Micro-B connector, which extends 0.05″ past the edge of the PCB.
2. Without included optional headers.